California is undergoing a major shift in how health care is delivered, financed, and sustained for rural communities, driven by state priorities and recent Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) announcements. In December 2025, CMS announced $50 billion in funding through the five-year Rural Health Transformation (RHT) Program, along with ACCESS and LEAD ACO. Additionally, the new mandatory TEAM model has launched in select counties, including San Diego, San Bernardino, Riverside, San Francisco, San Jose, Santa Rosa, San Luis Obispo, Hanford, Eureka, and Crescent City.
Led by the Department of Health Care Access and Information (HCAI), California’s RHT moves beyond short-term stabilization toward regional, coordinated care that addresses workforce shortages, long travel distances, hospital financial instability, and gaps in maternity and specialty care. Beginning in 2026, California will receive just over $233 million to expand access to care, strengthen workforce capacity, scale telehealth and e-consults, enhance data and cybersecurity, and improve regional collaboration and patient engagement.
RHT Focuses on Regional and Person-Centered Rural Care
California’s RHT initiative advances a regional, person-centered model through hub-and-spoke networks connecting rural hospitals, critical access hospitals, clinics, birthing centers, and specialty partners. To support this shift, the initiative focuses on three foundational areas:
- Workforce Development as the Foundation for Access: Recognizing that infrastructure alone cannot solve access challenges, the initiative places significant emphasis on workforce development through a comprehensive, statewide strategy focused on recruitment, training, and retention
- Modernizing Technology, Data, and Cybersecurity: Many rural providers continue to operate with limited interoperability, outdated electronic health records (EHRs), and insufficient cybersecurity protections. The initiative addresses these challenges through targeted investments in health information exchanges (HIEs) and patient-centered digital tools, with guidance from a dedicated Technical Assistance Center
- Rural Financial Stability and Accountability: Unlike prior rural funding efforts focused on short-term relief, California’s approach ties financial support to measurable system transformation and long-term sustainability. Rural hospitals will serve as regional anchors for care delivery while strengthening their own financial and operational stability
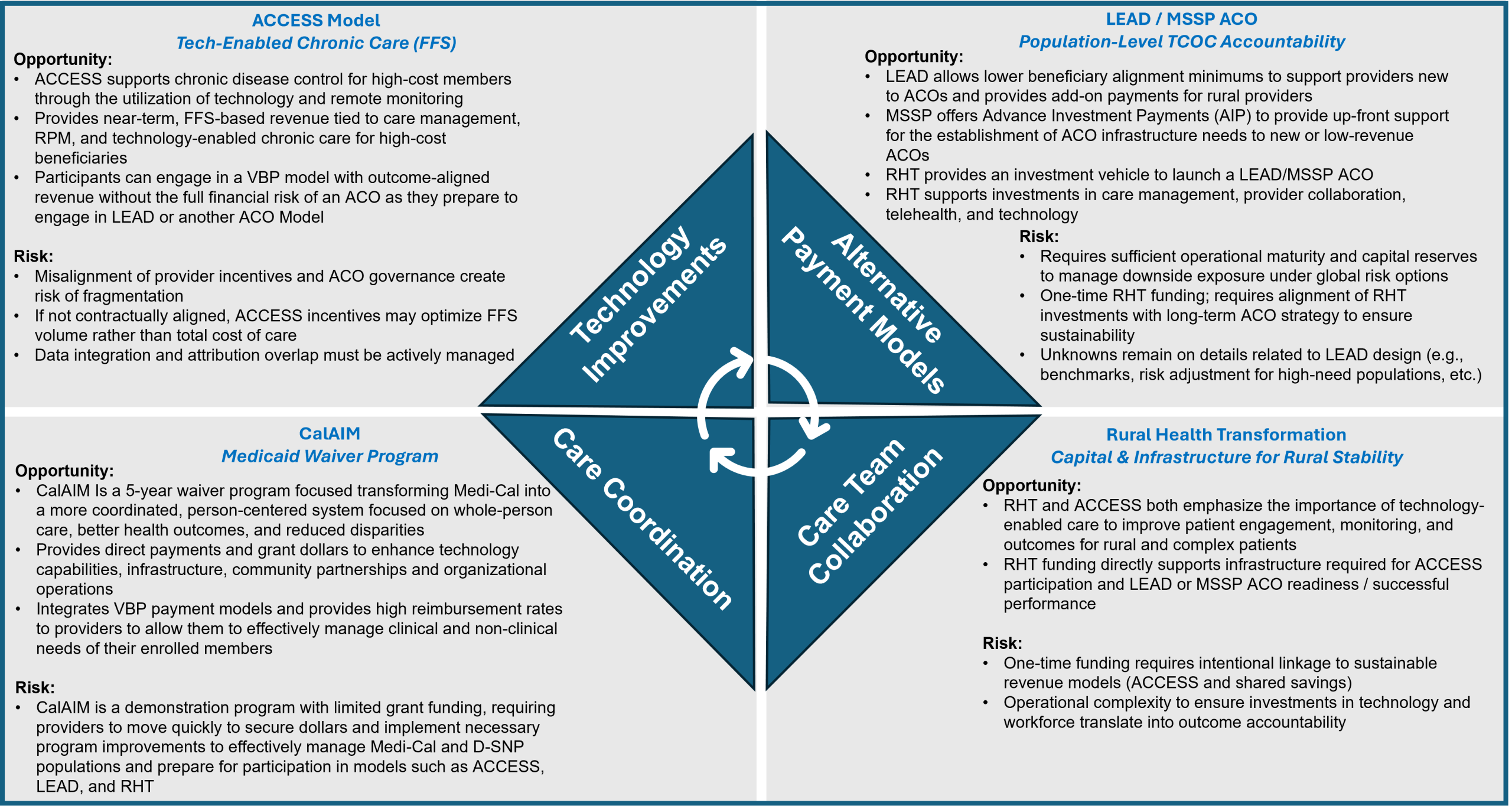
How Rural Health Transformation Aligns with ACCESS, LEAD, TEAM, and CalAIM
RHT aligns closely with federal and state reforms emphasizing accountability, equity, and value-based care:
- LEAD Program: Focuses on flexible payment models, specialty inclusion, technology, and care coordination. RHT mirrors this by building sustainable payment models while enhancing access to technology, care coordinators, and specialty providers
- TEAM Model: Improves care coordination for high-risk, post-acute patients that have recently undergone one of the identified procedures within the initiative (e.g., joint replacement, hip fracture, spinal fusion, major bowel procedures). RHT similarly prioritizes coordinated case management to reduce readmissions and complications
- ACCESS Model: Expands technology-supported care for chronic disease management. RHT similarly emphasizes advanced technology to enhance patient engagement, monitoring, and outcomes. At this time, ACCESS is a program providers would need to coordinate with rather than launch themselves, though guidelines and rules may evolve
- CalAIM: Provides a policy and financing foundation emphasizing population health, Enhanced Care Management, Community Supports, and value-based payment. RHT participants align care models, reporting, and quality measures with Medi-Cal requirements to reduce avoidable utilization, improve maternal and chronic disease outcomes, and address social determinants of health (SDOH)
Together, these programs are guiding California toward a health care system that keeps patients at the center while ensuring care is coordinated and financially sustainable.
For further details on ACCES, LEAD, and RHT from a federal standpoint, review this article Federal Healthcare Policy Updates Planning for Success in 2026-2027, written by our team of experts.
How to Prepare for Success in the RHT Program and TEAM, and What to Consider for MSSP or LEAD ACO Participation in Your Region
Success in California’s RHT Program and TEAM model requires early preparation and regional collaboration. Providers participating or considering participating in RHT or TEAM should focus on four key areas:
- Organizational Readiness: Manage population health, report outcomes, and incorporate person-generated data. CHS’ ARC platform integrates clinical, claims, and risk data to provide actionable insights, dashboards, and real-time performance monitoring
- Regional Partnerships: Build formal collaborations across hospitals, clinics, surgery centers, educational institutions, and community organizations. CHS supports strategic roadmaps, network optimization, and clinically integrated infrastructures
- Medi-Cal Alignment: Ensure care models, quality metrics, and reporting meet state goals and payment methodologies. CHS helps align performance metrics with quality and payment transformation initiatives
- Accountability and Sustainability: Develop operational plans, workflows, and workforce and technology strategies that sustain long-term improvements. CHS guides organizations in creating risk-aligned frameworks to maintain gains in access, quality, and financial outcomes
Looking Ahead: Long-Term Transformation for Rural Providers
California’s RHT initiative represents a shift from stand-alone operations toward regional alignment and shared responsibility. Success will increasingly depend on providers’ ability to collaborate, adopt technology, participate in workforce pipelines, and utilize data to demonstrate impact. Early engagement positions organizations to leverage transformation funding and remain viable as expectations evolve. With federal investment, state leadership, and regional collaboration, the program aims to reduce transportation burdens, stabilize essential providers, and improve outcomes for individuals and families with significant health needs. Rural health care organizations will benefit most by treating RHT as a catalyst for lasting transformation, rather than temporary funding.
For more information and to talk through your organization’s next move, reach out to us at info@copehealthsolutions.com or visit us at copehealthsolutions.com.


